What's SSL/TLS Certificate?
SSL/TLS Certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a domain's identity and enables an encrypted connection. SSL/TLS With TLS it is also desirable that a client connecting to a server is able to validate ownership of the server’s public key. This is normally undertaken using an X.509 digital certificate issued by a trusted third party known as a Certificate Authority (CA) which asserts the authenticity of the public key. In some cases, a server may use a self-signed certificate which needs to be explicitly trusted by the client, but this may be acceptable in private networks and/or where secure certificate distribution is possible. It is highly recommended though, to use certificates issued by publicly trusted CAs.
What's CA?
A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates conforming to the ITU-T's X.509 standard for Public Key Infrastructures (PKIs). Digital certificates certify the public key of the owner of the certificate (known as the subject), and that the owner controls the domain being secured by the certificate. A CA therefore acts as a trusted third party that gives clients (known as relying parties) assurance they are connecting to a server operated by a validated entity. End entity certificates are themselves validated through a chain-of-trust originating from a root certificate.
Root certificate trust is normally established through physical distribution of the root certificates in operating systems or browsers.
How to obtain SSL/TLS Certificate?
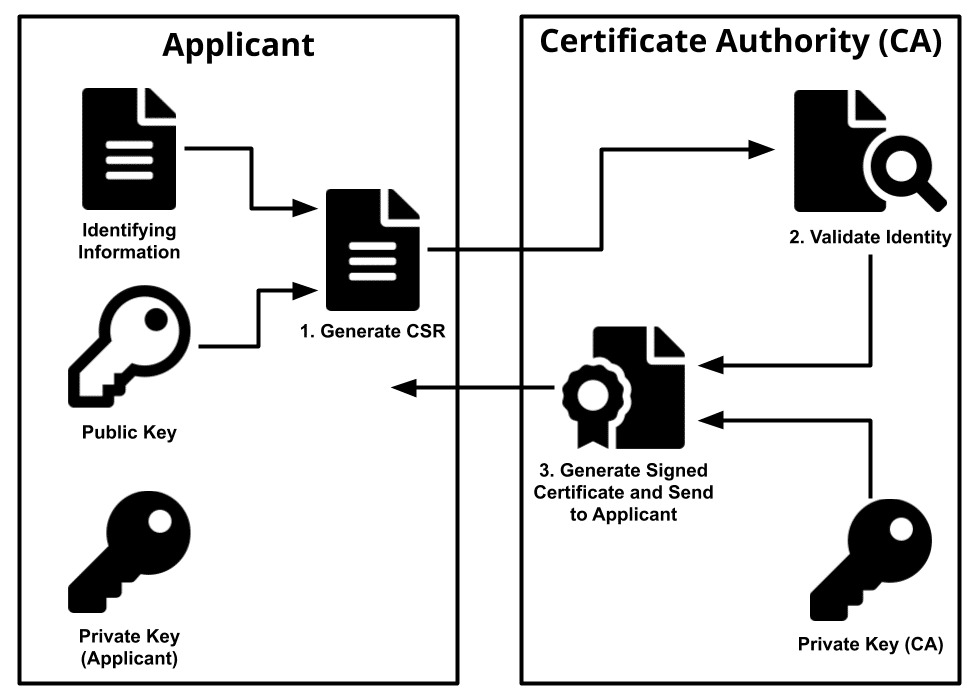
SSL certificates can be obtained directly from a Certificate Authority (CA) by generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for your server then submitting this to the Certificate Authority to validate your domain and company details. After certificate issued then install the certificate they provide once the process is complete.